-
 Help you save cost and time.
Help you save cost and time. -
 Provide reliable packaging for your goods.
Provide reliable packaging for your goods. -
 Fast and reliable delivery to save time.
Fast and reliable delivery to save time. -
 Excellent after-sales service.
Excellent after-sales service.
Industrial parts
Blog
Post
part number
Popular parts
Latest parts
-
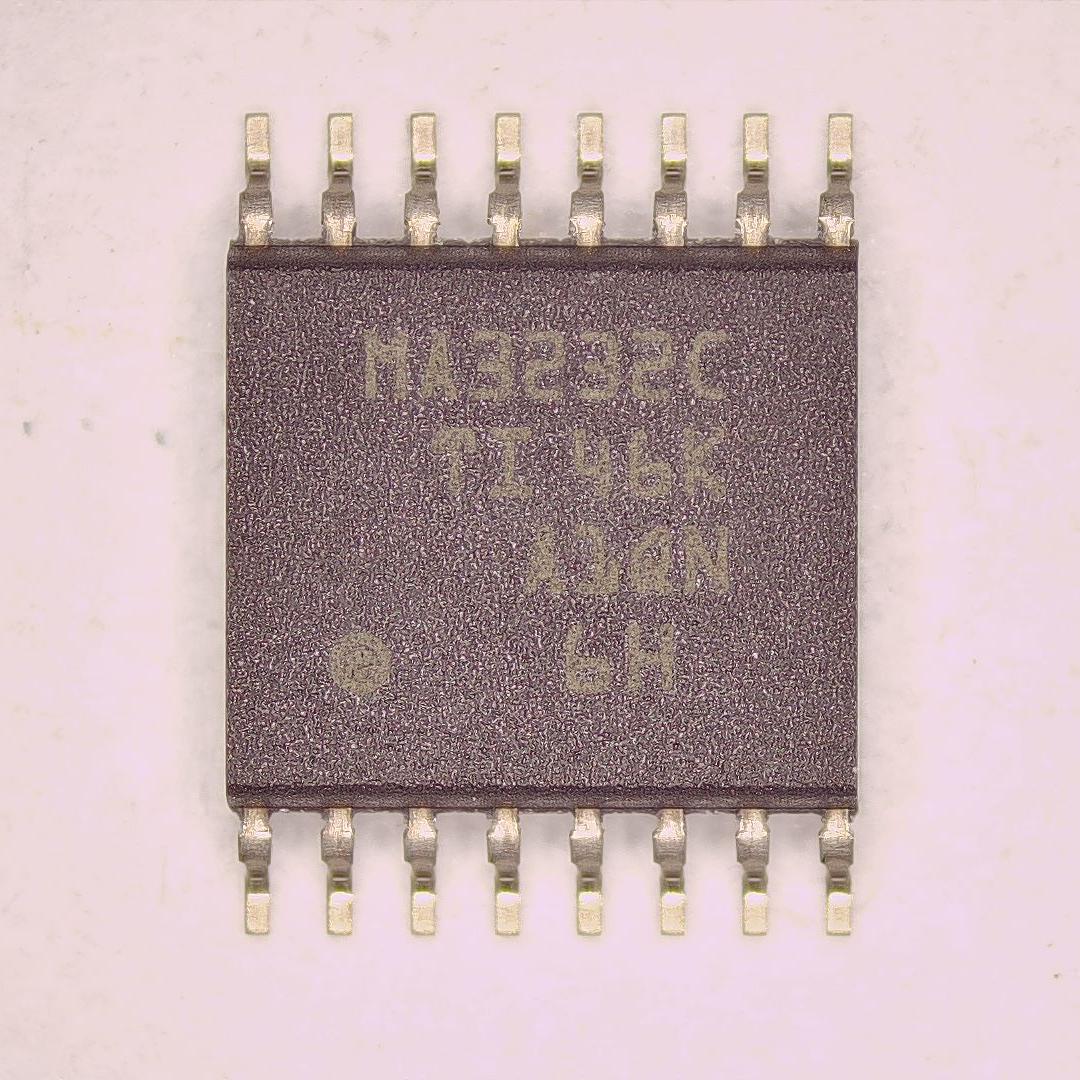
MAX3232CPWR
-
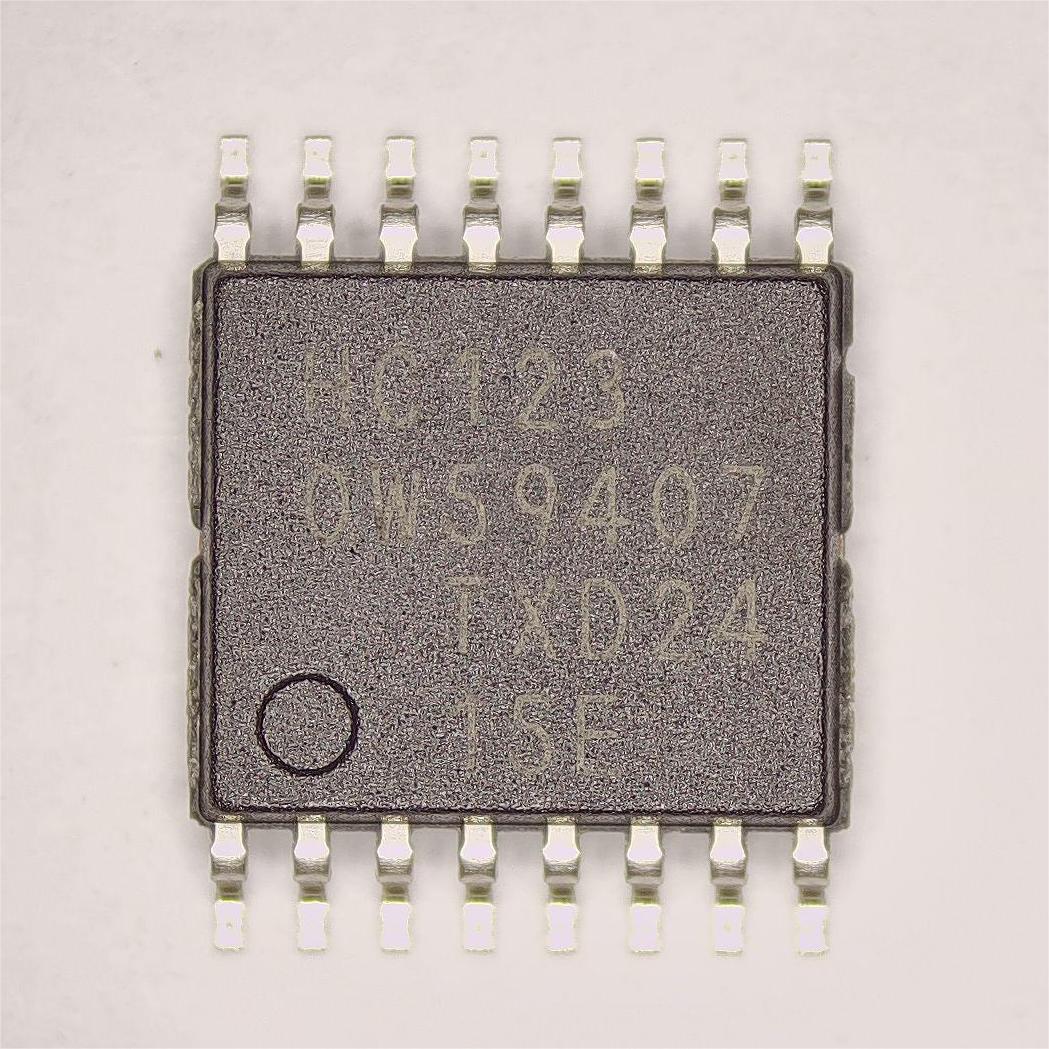
74HC123PW
-
SN74HC126PW
-
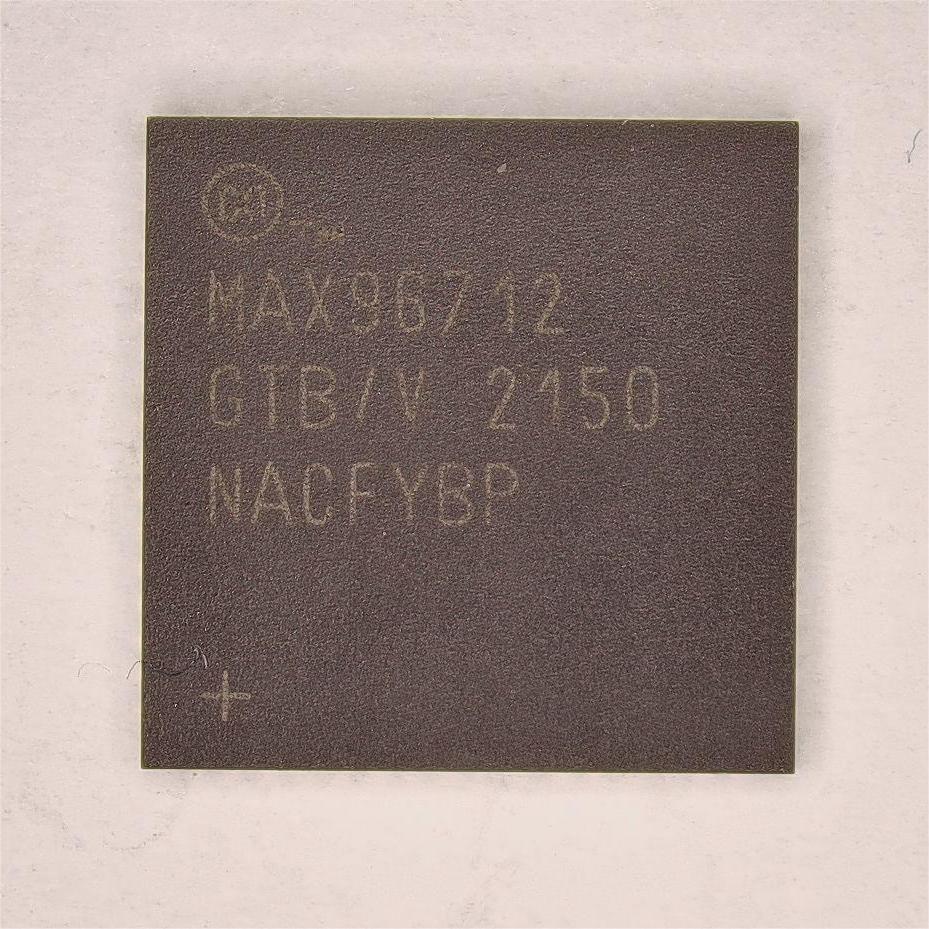
MAX96712GTBV+T
-
ADS1015IDGSR
-
88SE9235A1-NAA2C000
-
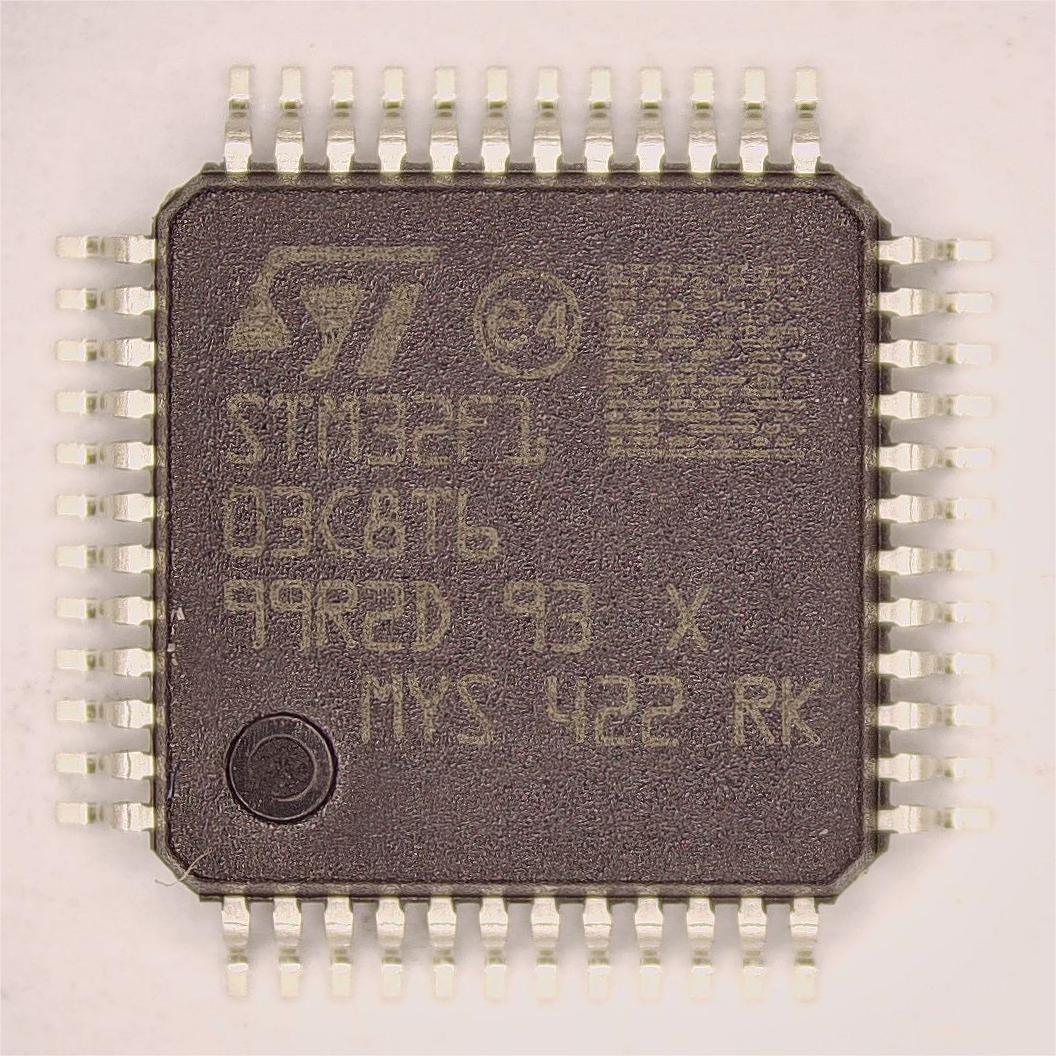
STM32F103C8T6
-
ADSP-21489BSWZ-4B
-
AD7606BSTZ
-
S432SYGWA/S530-E2
-
HMC1060LP3ETR
-
HMC833LP6GETR
-
LTM8023IY#PBF
-
LT3800EFE#PBF
-
MBR0540T1G
-
SA18N-20
-
SMW12TW1002
-
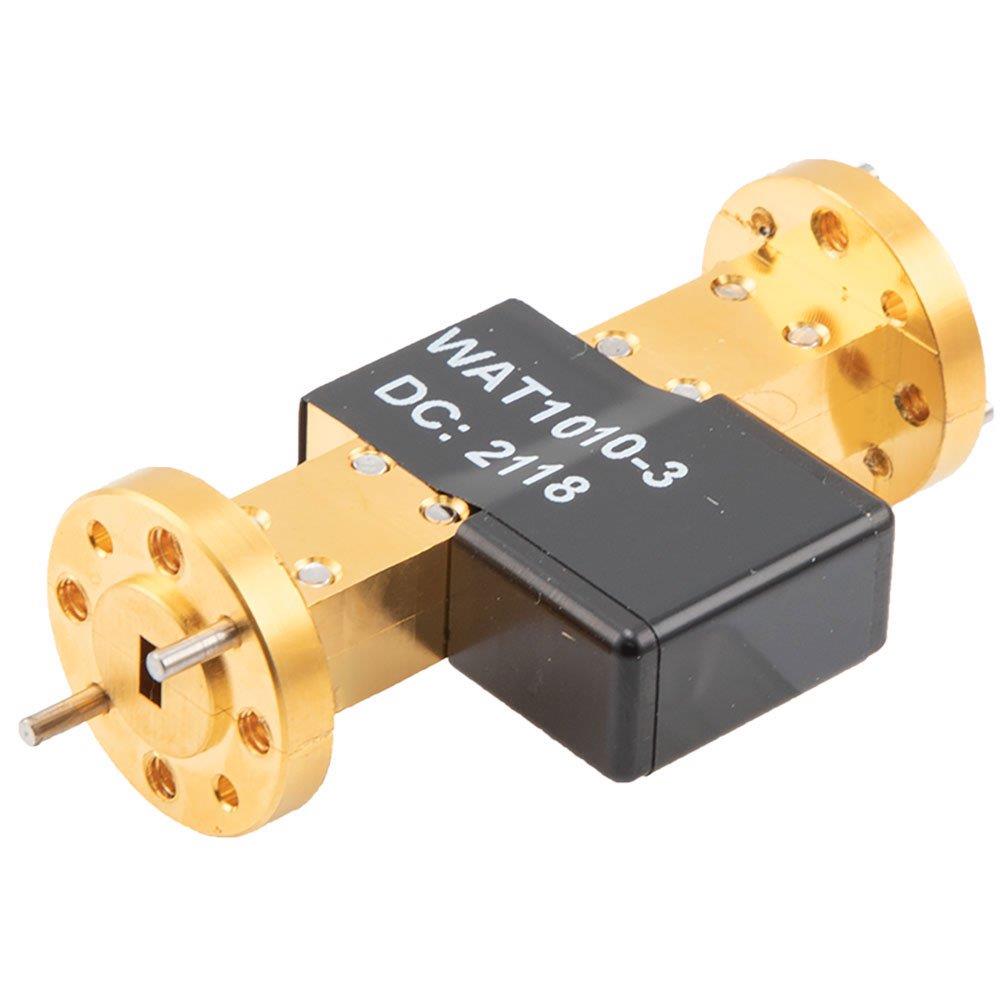
FMWAT1010-3
-
DSC1211NE3-C0021T
-
SMW137ACN
-
FM51OM1028
-
FMWGK1022
-
SA3N500-20
-
SH7219
-
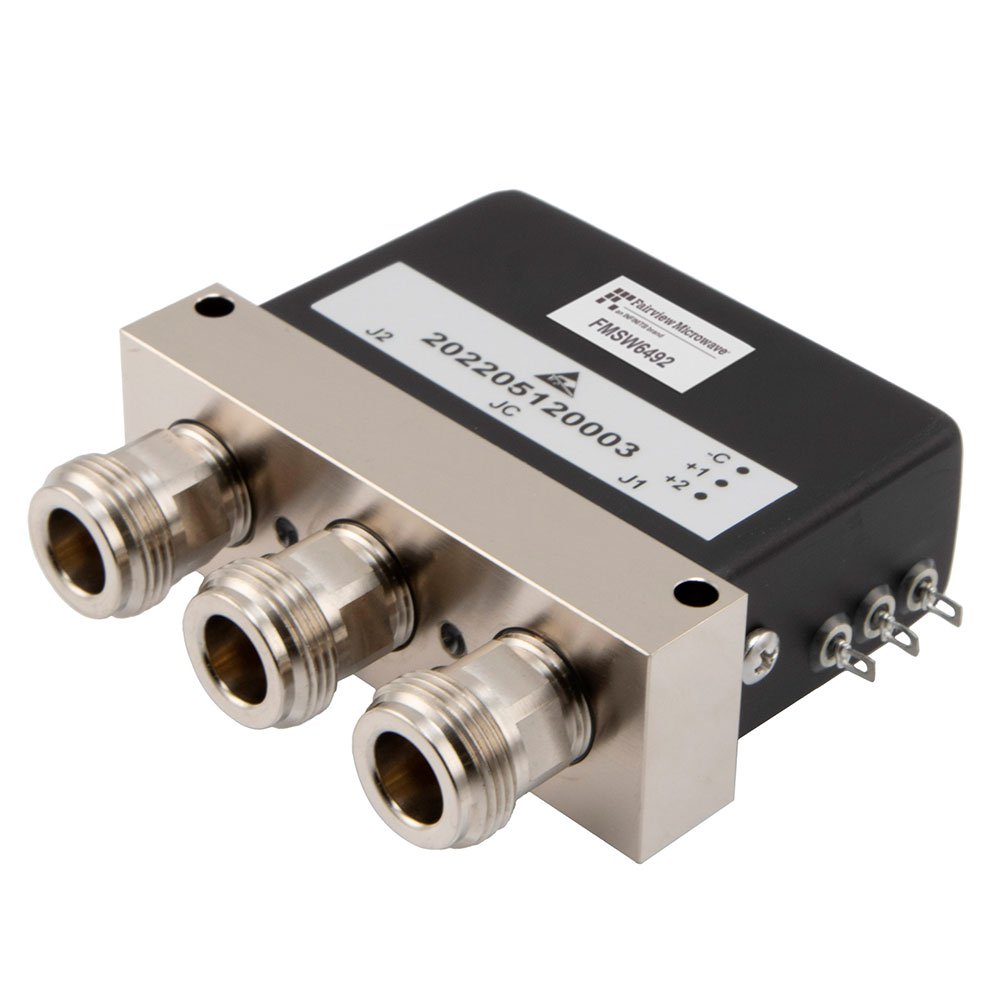
FMSW6492
-
SA3D100-03
-
FMWCA9809
-
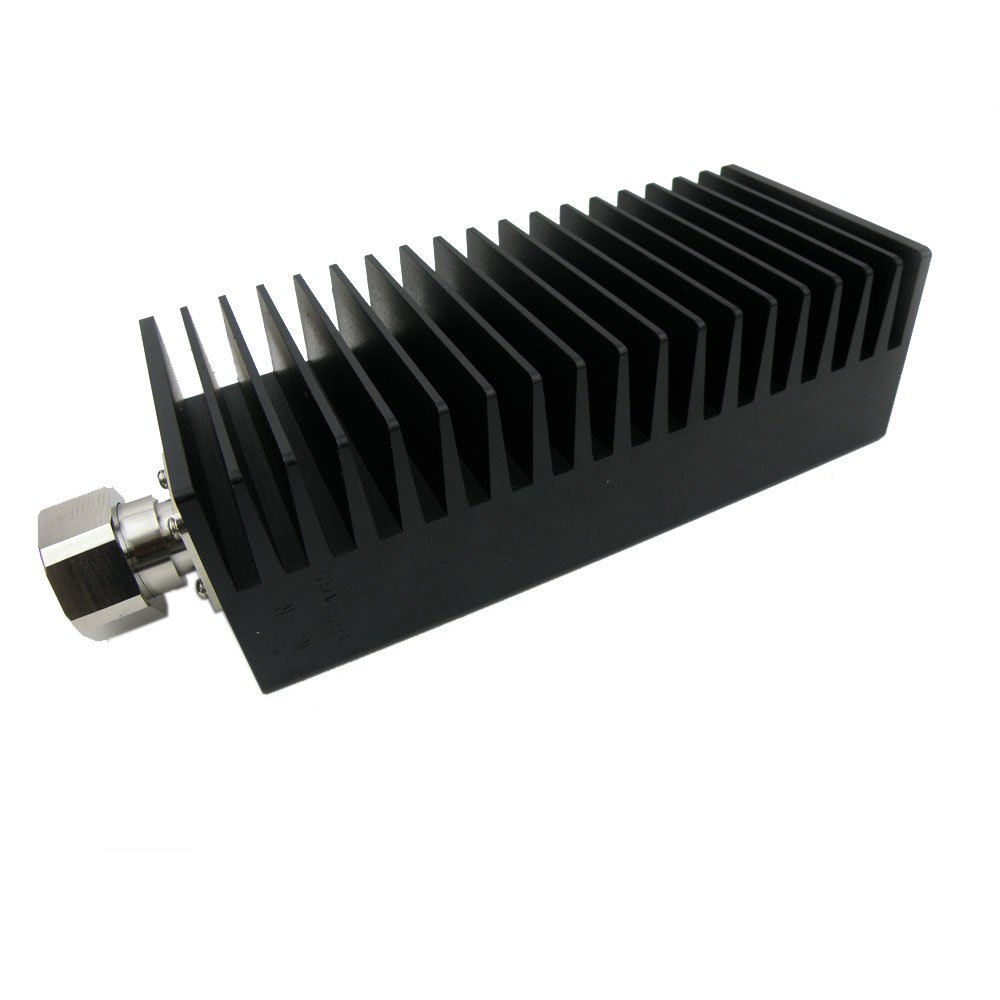
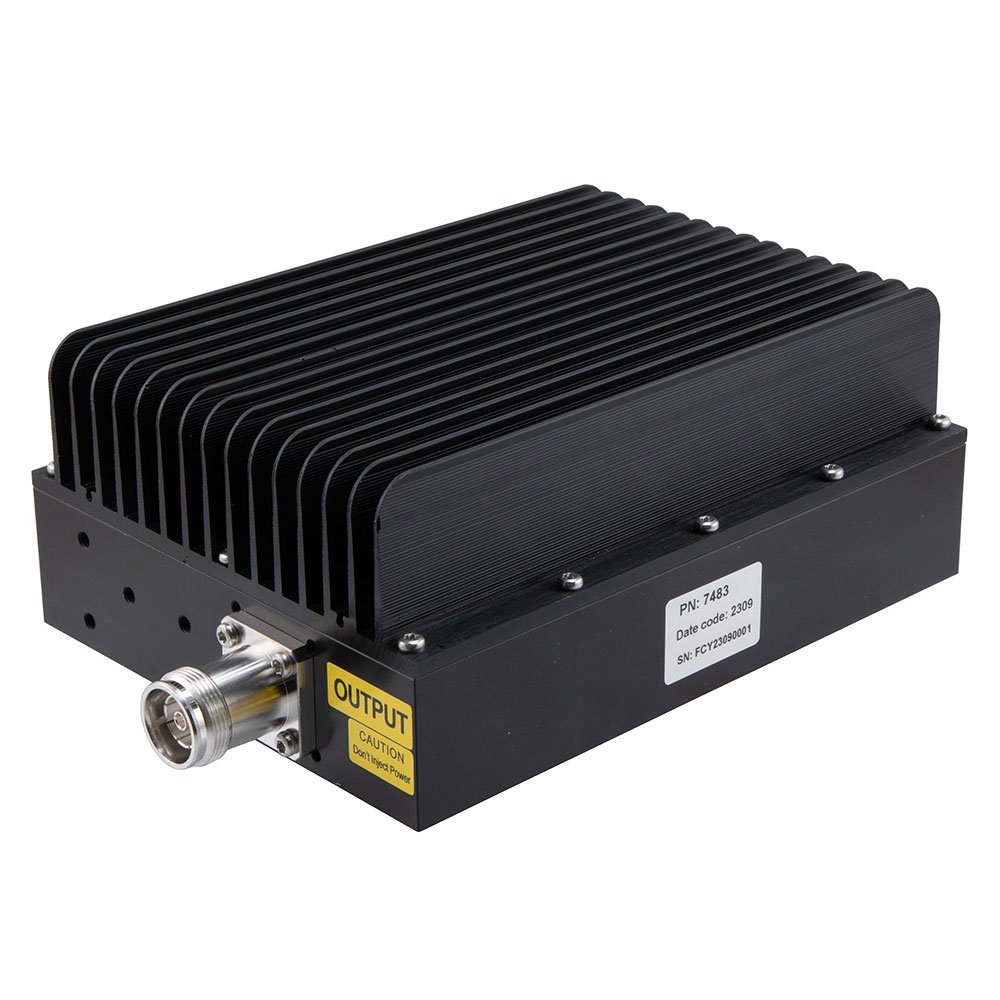
FMAT7483-10
-
FM9853B/SF-10
-
SI1591